Data-Driven Decision-Making: Accurate Customer Churn Prediction with Cat-Boost
Keywords:
CatBoost, Customer Retention, Stochastic Gradient Boost, PredictiveAnalysisAbstract
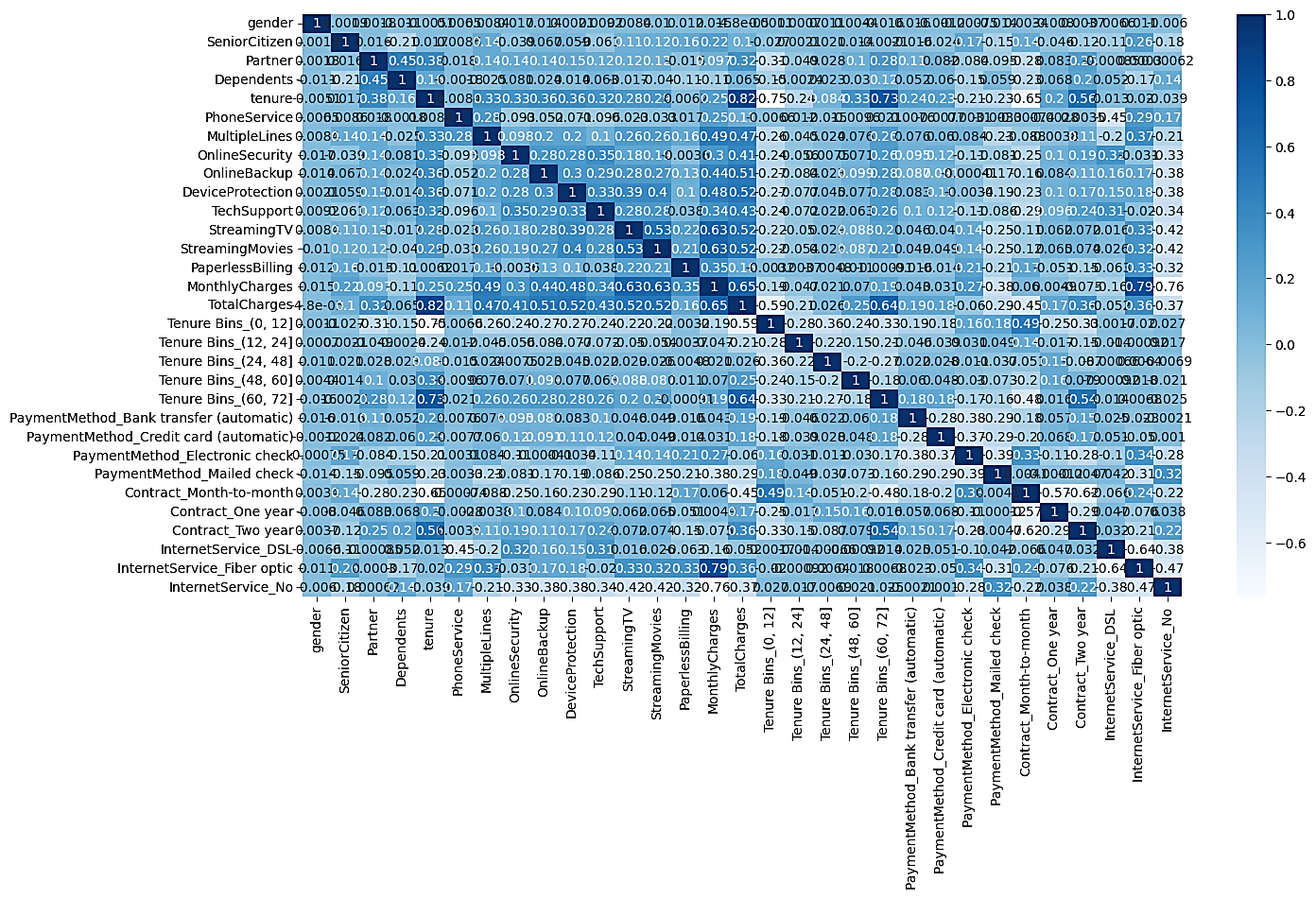
In the cutthroat telecommunications industry, customer churn poses a significant threat to profitability and brand reputation. To combat this, we propose a data-driven approach to predict churn, leveraging advanced Machine Learning (ML) algorithms on a comprehensive dataset of 7043 customer records with 21 features sourced from the IEEE website. By applying one-hot encoding to transform categorical data, we optimize ML algorithm performance. Our study pits three ML algorithms against each other: Cat Boost, Stochastic Gradient Boost, and Extreme Gradient Boost. The results are striking, with Cat Boost incipient as the top performer, boasting an impressive 94% accuracy, 90% precision, 97% recall, 94% F1-score, and an AUC of 0.94. These discoveries emphasize Cat Boost's extraordinary ability to predict churn, empowering telecom companies to proactively prevent attrition, target high-risk customers, and make data-driven decisions to make the most of profits. In today's speedily developing technical landscape, correctly predicting churn is critical to meeting the ever-changing potential of customers. Our research marks a noteworthy innovation in addressing churn trials, flooring the way for long-term accomplishment in the telecom industry.
Downloads